Managing Inflammation in Oral Tissues
Inflammation in oral tissues is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether caused by bacterial buildup, poor oral hygiene, or underlying health conditions, inflamed gums can lead to discomfort and more serious dental issues if left unaddressed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for gum inflammation is essential for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing long-term complications.
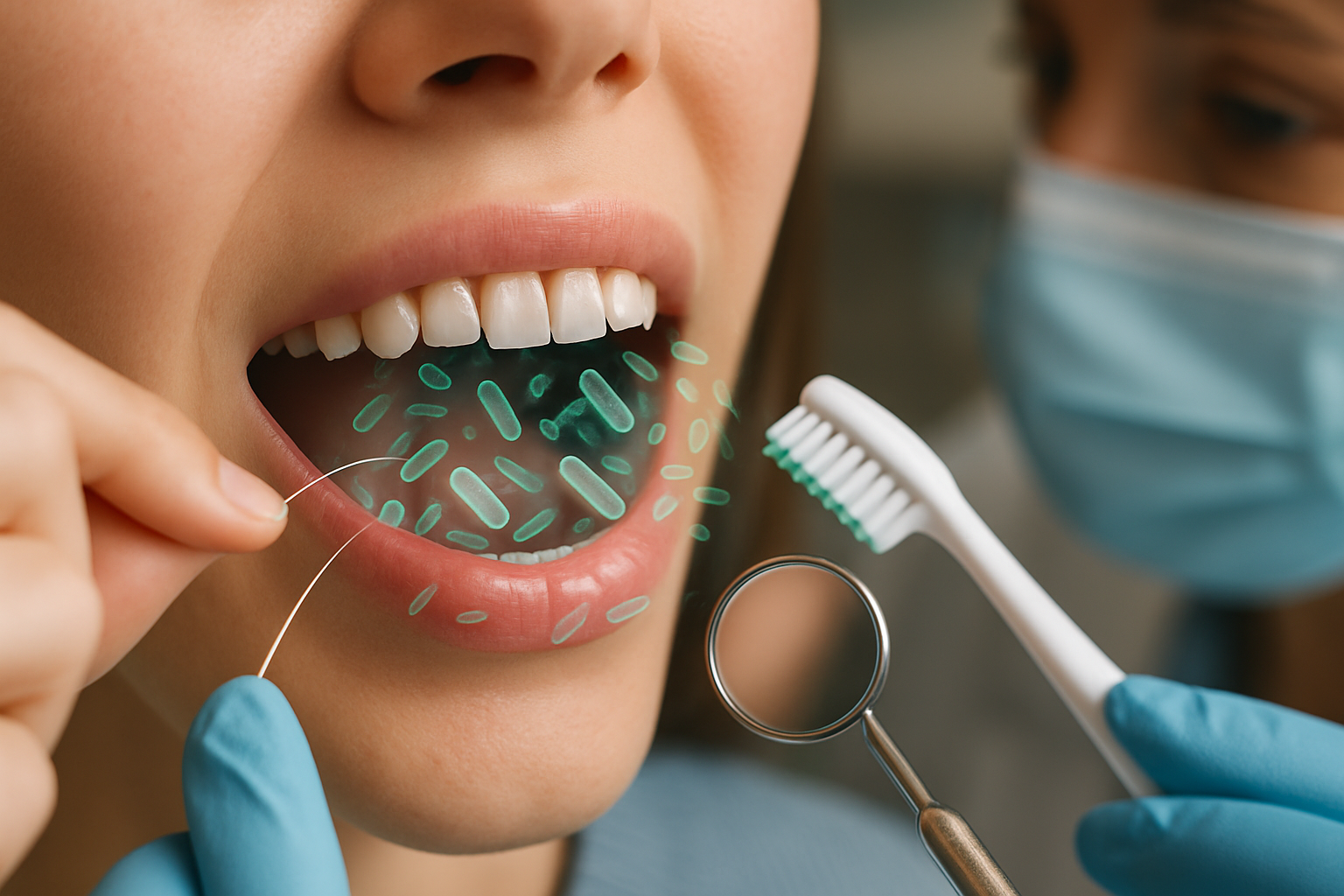
Gum inflammation, medically known as gingivitis in its early stages, represents one of the most prevalent oral health challenges faced globally. The condition occurs when bacteria accumulate along the gumline, triggering an immune response that causes redness, swelling, and tenderness. While mild inflammation may seem insignificant, it can progress to more severe periodontal disease if proper care is not implemented. Recognizing the signs early and taking appropriate action can preserve both gum health and overall wellbeing.
What Causes Inflammation in Oral Tissues?
The primary culprit behind gum inflammation is dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms continuously on teeth. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be eliminated through professional cleaning. Other contributing factors include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, nutritional deficiencies, and systemic conditions such as diabetes. Genetic predisposition also plays a role in determining individual susceptibility to gum problems. Understanding these risk factors helps in developing targeted prevention strategies tailored to personal circumstances.
How Can You Recognize Early Signs of Gum Problems?
Early detection of gum inflammation significantly improves treatment outcomes. Common symptoms include bleeding during brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gumlines, and visible redness or swelling around teeth. Some individuals may experience tenderness when chewing or notice changes in how their teeth fit together. In advanced cases, pockets may form between teeth and gums, creating spaces where bacteria thrive. Regular self-examination combined with professional dental assessments ensures that issues are identified before they escalate into more complex conditions requiring intensive intervention.
What Are Effective Management Strategies for Gum Health?
Managing gum inflammation involves a multi-faceted approach combining home care practices with professional interventions. Daily oral hygiene routines should include brushing at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing to remove debris between teeth, and using antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial load. Professional cleanings every six months help remove tartar buildup that home care cannot address. For moderate to severe cases, dental professionals may recommend scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that smooths tooth roots and removes bacteria from below the gumline. In some situations, antibiotic therapy or surgical treatments may be necessary to restore gum health and prevent tooth loss.
How Does Lifestyle Impact Oral Tissue Health?
Lifestyle choices significantly influence gum health outcomes. Smoking and tobacco use dramatically increase inflammation risk and impair healing processes. A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and antioxidants supports tissue repair and immune function. Stress management is equally important, as chronic stress can weaken immune responses and contribute to inflammation throughout the body, including oral tissues. Staying hydrated helps maintain saliva production, which naturally cleanses the mouth and neutralizes harmful acids. Regular exercise improves circulation, delivering essential nutrients to gum tissues and promoting overall oral health.
What Role Do Professional Treatments Play?
Professional dental care forms the cornerstone of comprehensive gum health management. Dental hygienists and dentists possess specialized tools and expertise to address issues that home care cannot resolve. During routine visits, professionals assess gum pocket depths, check for signs of bone loss, and evaluate overall oral health status. They can identify early warning signs that patients might overlook and provide personalized recommendations based on individual risk factors. Advanced treatments such as laser therapy, tissue grafts, or regenerative procedures may be suggested for severe cases. Establishing a collaborative relationship with dental care providers ensures continuity of care and optimal long-term outcomes.
Can Gum Health Affect Overall Wellbeing?
Research increasingly demonstrates connections between oral health and systemic conditions. Chronic gum inflammation has been linked to cardiovascular disease, diabetes complications, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. The inflammatory response triggered by gum disease can affect distant organs and systems through the bloodstream. Conversely, managing gum health may contribute to better control of chronic conditions and improved quality of life. This interconnection underscores the importance of viewing oral care as an integral component of holistic health management rather than an isolated concern.
Addressing inflammation in oral tissues requires commitment to consistent preventive care, prompt attention to warning signs, and collaboration with dental professionals. By understanding the causes and implementing evidence-based management strategies, individuals can maintain healthy gums throughout their lives. Regular monitoring, proper hygiene practices, and lifestyle modifications work together to prevent minor issues from developing into serious complications. Taking proactive steps today protects not only oral health but also contributes to overall physical wellbeing and confidence in daily life.