Key Symptoms That May Reveal Diabetes in Early Stages
Recognizing diabetes in its early stages can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively. Many people live with undiagnosed diabetes for years, missing crucial opportunities for early intervention. Understanding the warning signs your body sends can help you seek medical attention before complications develop. From subtle changes in energy levels to more noticeable symptoms like increased thirst, your body provides important clues about blood sugar irregularities. Early detection allows for better treatment outcomes and can prevent serious health complications down the road.
Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, yet many cases remain undiagnosed until complications arise. The condition develops gradually, often presenting subtle warning signs that can be easily overlooked or attributed to other factors like stress, aging, or lifestyle changes. Understanding these early indicators can be crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
18 Signs of Diabetes to Watch For
The early symptoms of diabetes can vary from person to person, but certain patterns emerge consistently. Excessive thirst and frequent urination often appear together as your kidneys work harder to filter excess glucose from your blood. You might find yourself drinking more water than usual yet still feeling thirsty, or needing to use the bathroom more frequently, especially at night.
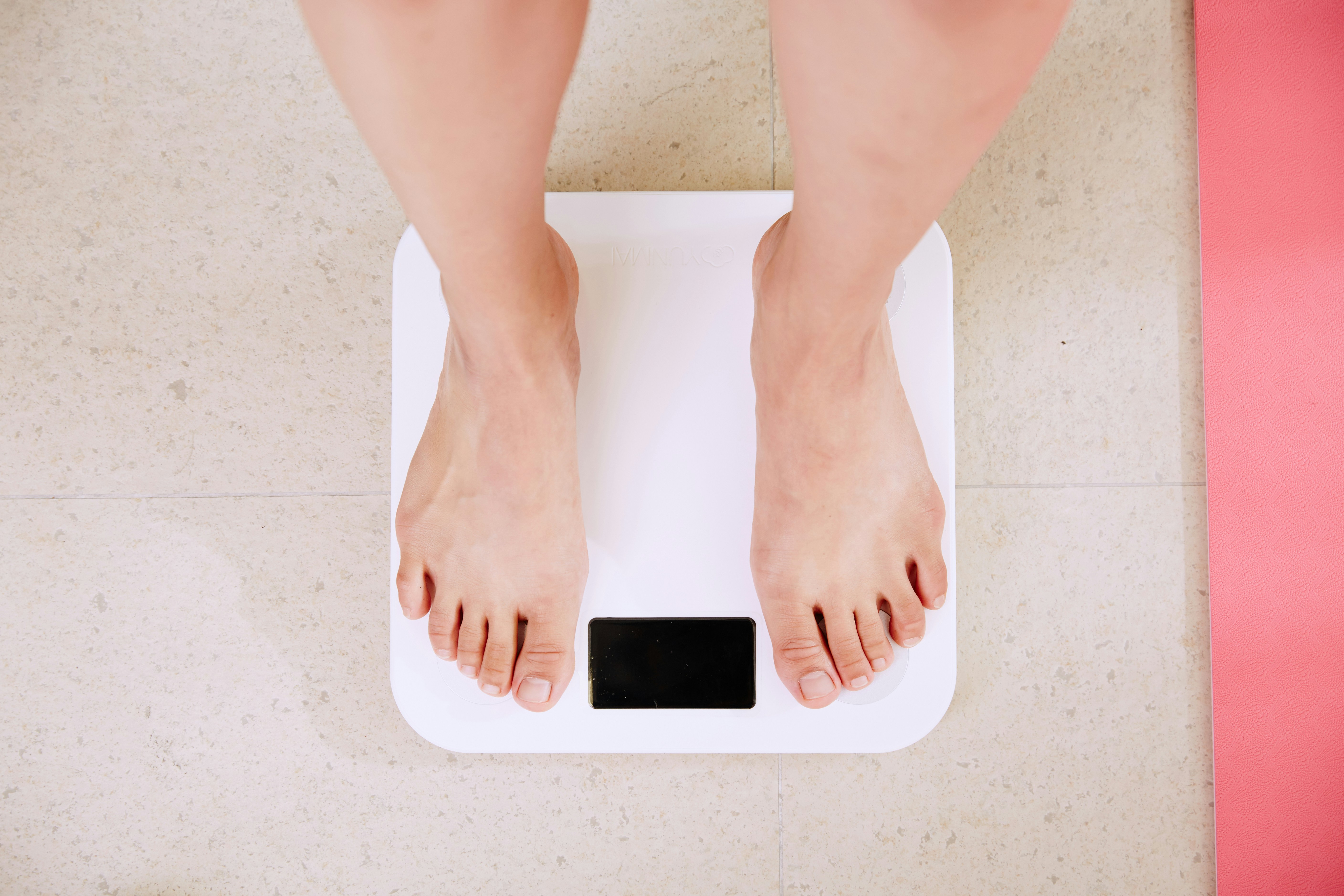
Unexplained weight loss despite normal or increased appetite can signal that your body cannot properly use glucose for energy. Fatigue and weakness may develop as your cells struggle to access the fuel they need. Blurred vision occurs when high blood sugar levels cause the lens in your eyes to swell, affecting your ability to focus clearly.
Slow-healing cuts and wounds, frequent infections, and tingling or numbness in hands and feet indicate that elevated blood sugar is affecting your circulation and immune system. Dark patches of skin, particularly around the neck or armpits, may also appear as an early warning sign.
Early Signs of Diabetes in Daily Life
Many early diabetes symptoms manifest in ways that can easily be dismissed as normal life stresses. Increased hunger, even after eating, occurs because your cells cannot access glucose effectively. You might experience mood changes, irritability, or difficulty concentrating as your brain struggles with inconsistent fuel supply.
Skin problems become more common, including dry skin, itching, or recurring infections like yeast infections. Your gums might become tender or swollen, and you may notice a fruity smell on your breath. These seemingly unrelated symptoms often occur together, creating a pattern that healthcare providers can recognize.
Changes in your eating patterns, sleep quality, and energy levels throughout the day can also provide important clues. Many people report feeling particularly tired after meals or experiencing energy crashes that seem disproportionate to their activity level.
18 Signs of Diabetes and Treatments Available
When multiple symptoms appear together, medical evaluation becomes essential. Healthcare providers use various tests to diagnose diabetes, including fasting blood glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1C measurements. Early diagnosis opens the door to numerous treatment options that can effectively manage the condition.
Treatment approaches vary depending on the type of diabetes and individual circumstances. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy, while Type 2 diabetes may be managed through lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin, depending on the severity and progression of the condition.
Lifestyle interventions play a crucial role in diabetes management regardless of type. Dietary modifications, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction can significantly improve blood sugar control and overall health outcomes.
| Treatment Category | Options Available | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Changes | Diet modification, exercise, weight management | Improves insulin sensitivity, reduces complications |
| Oral Medications | Metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors | Helps control blood sugar levels |
| Injectable Treatments | Insulin, GLP-1 agonists | Direct blood sugar control, weight management |
| Monitoring Tools | Glucose meters, continuous monitors | Real-time blood sugar tracking |
Understanding Risk Factors and Prevention
Certain factors increase your likelihood of developing diabetes, including family history, age, ethnicity, and lifestyle factors. Being overweight, leading a sedentary lifestyle, or having conditions like high blood pressure or polycystic ovary syndrome can elevate your risk.
While some risk factors cannot be changed, many are modifiable through lifestyle choices. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, and managing stress can significantly reduce your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Regular health screenings become increasingly important as you age or if you have multiple risk factors. Healthcare providers can detect prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet in the diabetic range, allowing for early intervention to prevent progression.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience multiple symptoms consistently over several weeks, scheduling a medical evaluation is important. Do not wait for symptoms to become severe or numerous before seeking help. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Emergency medical attention is necessary if you experience symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis, including severe dehydration, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, or difficulty breathing. These symptoms indicate a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
Regular communication with healthcare providers allows for ongoing monitoring and treatment adjustments as needed. Diabetes management is most effective when approached as a collaborative effort between patients and their medical team.
Recognizing the early signs of diabetes empowers you to take control of your health before complications develop. While the symptoms can seem overwhelming, effective treatments and management strategies allow millions of people to live full, healthy lives with diabetes. The key lies in early recognition, prompt medical attention, and commitment to ongoing management strategies tailored to your individual needs.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.