Best Plasma Donation Center Guide
Finding the best plasma donation center involves more than spotting a convenient address. It means weighing safety standards, fair compensation, donor eligibility policies, and the overall donor experience. This guide walks through how centers operate, what sets trustworthy locations apart, and how center comparison can help align personal priorities with community impact and health considerations.
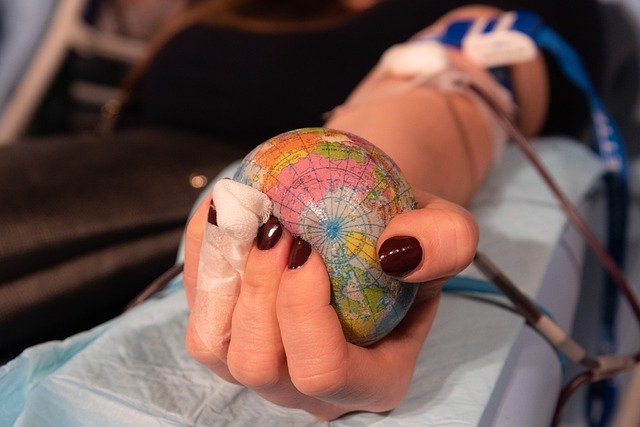
Plasma donation has become an increasingly important aspect of healthcare, supporting the production of medications and treatments for patients with rare and chronic conditions. As more people consider becoming plasma donors, understanding the process and what plasma donation centers offer becomes essential for making an informed choice.
Understanding Plasma Donation Center Basics
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood that contains proteins, antibodies, and clotting factors essential for various medical treatments. Plasma donation centers are specialized facilities where donors can safely give plasma through a process called plasmapheresis. During this procedure, blood is drawn from the donor, plasma is separated using a machine, and the remaining blood components are returned to the donor’s body. This process typically takes longer than whole blood donation, usually between 60 to 90 minutes. Plasma donation centers operate under strict regulatory guidelines established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure donor safety and product quality. Donors must meet specific health requirements, including age restrictions (typically 18 years or older), weight minimums (usually at least 110 pounds), and pass health screenings that include testing for infectious diseases. Most centers allow donors to give plasma up to twice per week, with at least one day between donations.
Why People Choose Plasma Donation Centers
Individuals donate plasma for various reasons, with compensation being a significant motivator for many donors. Unlike whole blood donation, which is typically unpaid, plasma donation centers often provide financial compensation to donors for their time and contribution. This compensation helps cover the donor’s time commitment and any inconvenience associated with the donation process. Beyond financial reasons, many donors are motivated by the knowledge that their plasma helps create medications for patients with immune deficiencies, bleeding disorders, and other serious medical conditions. Plasma-derived therapies treat conditions such as hemophilia, primary immunodeficiency diseases, and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. The accessibility of plasma donation centers also makes it convenient for people who want to contribute regularly to medical research and treatment development. Some donors appreciate the health screening benefits, as each donation includes basic health checks that can help monitor their wellness over time.
Benefits of Donating at Plasma Centers
Donating plasma offers multiple advantages for both donors and the broader medical community. For donors, the most immediate benefit is often the compensation received, which varies by location and center but can provide supplemental income. Regular donors may receive bonuses for consistent donations or referral incentives for bringing new donors to the center. From a health perspective, donors receive mini-physical examinations before each donation, including blood pressure checks, pulse readings, temperature measurements, and protein level testing. These routine screenings can help donors stay aware of their general health status. The plasma itself is used to manufacture critical medications that cannot be synthesized artificially, making each donation potentially life-saving for patients who depend on plasma-derived therapies. Additionally, the donation process is relatively safe when performed at licensed facilities with trained staff and proper equipment. Many donors also report a sense of personal satisfaction knowing their contribution helps others in need, creating a positive social impact alongside any financial benefits.
Understanding the Plasma Donation Process Steps
The plasma donation process follows a structured sequence designed to ensure donor safety and plasma quality. First-time donors begin with registration, which includes providing identification, completing a detailed health questionnaire, and undergoing a physical examination. This initial screening may take additional time but is streamlined for return donors. Before each donation, staff members conduct a mini-physical to verify the donor meets current health standards. Once cleared, the donor proceeds to the donation floor where a phlebotomist inserts a sterile needle into a vein, usually in the arm. The plasmapheresis machine then draws blood, separates the plasma, and returns red blood cells and other components back to the donor in cycles. Throughout the 60 to 90-minute process, staff members monitor donors for any adverse reactions. After donation completion, donors rest briefly in a recovery area and receive their compensation, typically loaded onto a prepaid debit card. Centers provide guidance on post-donation care, including staying hydrated and avoiding strenuous activity for several hours.
Compensation and Center Comparisons
Plasma donation compensation varies significantly depending on location, center policies, and donor frequency. Understanding typical payment structures can help potential donors make informed decisions about where to donate.
| Center Type | Typical Payment Range | Frequency Bonuses | Special Promotions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large National Chains | $50-$100 per donation | Yes, for regular donors | New donor bonuses up to $1,000 in first month |
| Regional Centers | $40-$80 per donation | Limited programs | Occasional referral bonuses |
| Independent Facilities | $30-$70 per donation | Varies by location | Seasonal promotions |
Compensation rates reflect the time commitment required and local market conditions. First-time donors often receive higher payments during their initial donations as an incentive to return. Regular donors who maintain consistent schedules may qualify for loyalty bonuses or increased per-donation rates.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Common Challenges at Plasma Donation Centers
While plasma donation is generally safe, donors may encounter various challenges during their experience. Wait times can be significant, especially at busy centers or during peak hours, with some donors spending two to three hours at the facility for a single donation. Vein issues present another common challenge, as repeated donations can make it harder for phlebotomists to locate suitable veins, potentially causing discomfort or requiring multiple needle sticks. Some donors experience side effects such as dehydration, fatigue, dizziness, or bruising at the needle site. More serious but rare reactions include citrate reactions (tingling sensations from the anticoagulant used) or vasovagal responses (fainting). Eligibility requirements can also pose challenges, as temporary deferrals occur for reasons like low protein levels, recent tattoos, travel to certain countries, or medication use. The time commitment required for regular donations can be difficult for people with demanding work schedules or family obligations. Additionally, some donors find the repetitive nature of frequent donations physically draining over time, requiring them to adjust their donation frequency or take breaks to recover.
Understanding these aspects of plasma donation helps potential donors set realistic expectations and prepare adequately for their donation experience. By choosing reputable centers and following proper pre- and post-donation care guidelines, donors can contribute to life-saving treatments while minimizing potential challenges.